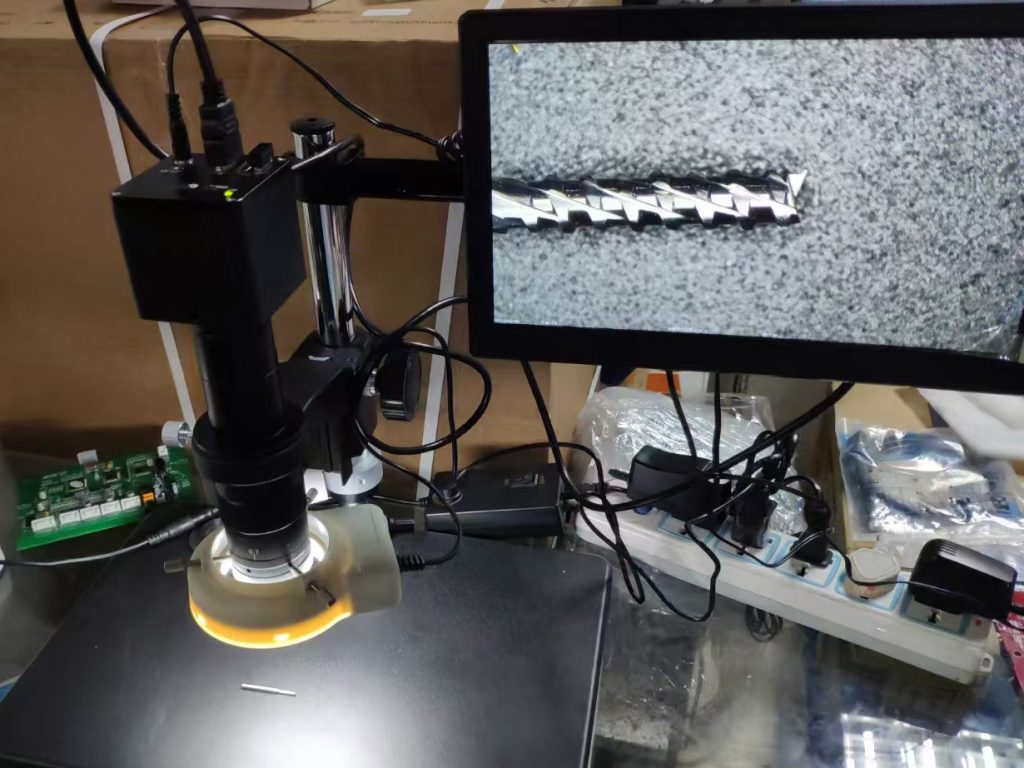
The application of industrial microscope cameras in metallographic microscopes is mainly to improve the efficiency and accuracy of metallographic analysis through high-resolution imaging and digital technology. The following are specific application scenarios and examples:
1. Material microstructure analysis
Application scenario: Observe the microstructures such as grain size, phase distribution, and defects of metals, alloys, and other materials.
Example:
In steel production, industrial microscope cameras can take high-resolution metallographic images to analyze the grain size and distribution of steel and evaluate its mechanical properties (such as strength and toughness). Through digitized images, image analysis software can be used to automatically measure grain size and improve analysis efficiency.
2. Failure analysis
Application scenario: Analyze the causes of failure of metal parts, such as cracks, fatigue, corrosion, etc.
Example:
A mechanical part breaks during use. By combining a metallographic microscope with an industrial camera to take a high-definition image of the fracture, the origin and extension path of the crack can be clearly observed, and the cause of failure (such as stress concentration, material defects, etc.) can be further determined by combining energy spectrum analysis (EDS).
3. Quality control and inspection
Application scenario: Quality inspection of metal materials during the production process to ensure that they meet the standards.
Example:
In the aluminum alloy casting process, the industrial microscope camera can take real-time metallographic images of the castings to detect defects such as pores and inclusions to ensure that the product quality meets industry standards (such as aerospace material standards).
4. Coating and surface treatment analysis
Application scenario: Observe the thickness, uniformity and bonding of the metal surface coating or treatment layer.
Example:
In the chrome plating of automotive parts, the industrial microscope camera can take cross-sectional images of the coating, measure the thickness of the coating and observe its bonding with the substrate to ensure that the coating quality meets the requirements of corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
5. Research and development
Application scenario: In the research and development of new materials, observe the microscopic changes in the material.
Example:
When developing new high-temperature alloys, the industrial microscope camera can record the metallographic changes of the material under different heat treatment conditions, helping researchers optimize the heat treatment process and improve the high-temperature performance of the material.
6. Teaching and training
Application scenario: used for teaching and training of metallography, showing typical metallographic structures.
Example:
In the experimental class of materials science and engineering major in colleges and universities, industrial microscope cameras can project the metallographic structures of typical metals (such as cast iron and stainless steel) onto a large screen or computer, which is convenient for students to observe and learn.
7. Automated detection
Application scenario: combined with image processing software, the automated analysis of metallographic structures can be realized.
Example:
In the detection of mass-produced metal materials, industrial microscope cameras can automatically take metallographic images of a large number of samples, and automatically count parameters such as grain size and phase ratio through image analysis software, greatly improving the detection efficiency.
Summary
Industrial microscope cameras are widely used in metallographic microscopes, covering many fields such as material analysis, failure analysis, quality control, research and development, and teaching. Its high-resolution imaging and digitalization functions not only improve the accuracy of metallographic analysis, but also realize automated detection and efficient data processing, providing important support for materials science and industrial production.